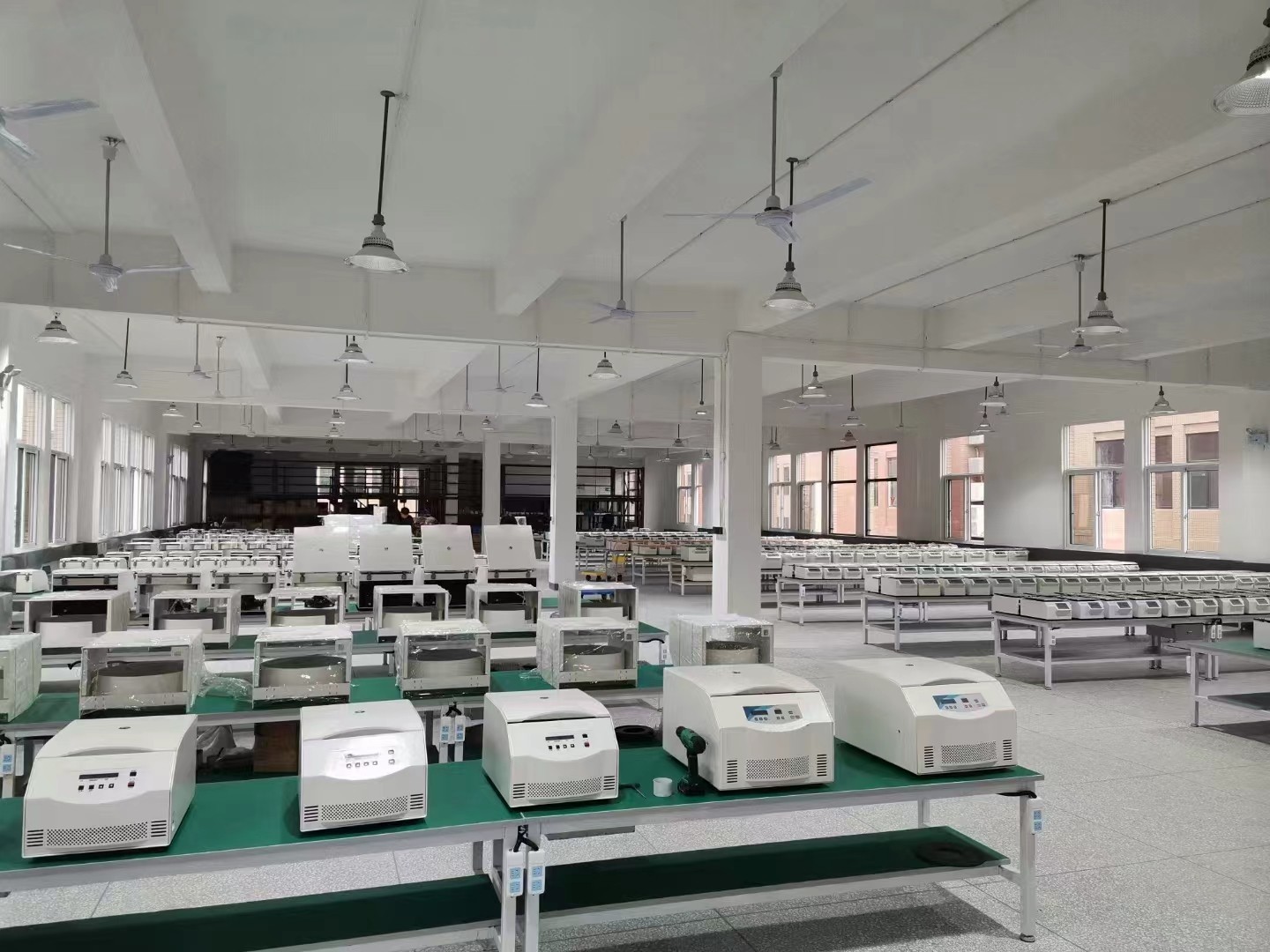

How to control the quality of centrifuge from the aspects of design, production, supplier and after-sales service?
2024-08-29 15:42How to control the quality of centrifuge from the aspects of design, production, supplier and after-sales service?
Controlling the quality of centrifuges as a professional manufacturer involves implementing a comprehensive and systematic approach to ensure that every unit meets high standards of performance, reliability, and safety. In our company this process requires careful attention to design, material selection, manufacturing processes, testing, and continuous improvement.
We have several steps as a detailed guide on how to control centrifuge quality.
1. Design and Engineering Control
a. Understanding Requirements:
Begin with a thorough understanding of the intended application of the centrifuge. Whether for laboratory use, industrial processing, or medical applications, each centrifuge must be designed to meet specific performance criteria.
Collaborate with clients and industry experts to gather precise requirements, including speed (RPM), capacity, temperature control, and safety features.
b. Design Specifications:
Develop detailed design specifications that include material selection, dimensional tolerances, motor and drive system requirements, and electronic control systems.
Use advanced CAD software to create precise designs that consider stress points, vibration control, and aerodynamics.
c. Prototyping and Testing:
Build prototypes to test the design under real-world conditions. This step helps identify potential issues early in the development process.
Conduct simulations and physical testing to verify that the design meets all functional and safety requirements.
2. Material Selection and Supplier Quality Control
a. Selecting High-Quality Materials:
Choose materials that offer durability, resistance to corrosion, and appropriate mechanical properties. For example, stainless steel is often used for its strength and corrosion resistance.
Consider the compatibility of materials with the samples or substances that the centrifuge will process, especially in laboratory and medical applications.
b. Supplier Qualification:
Establish a rigorous supplier qualification process to ensure that all raw materials and components meet the required standards.
Conduct regular audits of suppliers to verify compliance with quality, ethical, and environmental standards.
c. Incoming Inspection:
Implement a strict incoming inspection protocol to check the quality of materials and components before they enter the production process.
Use precision measurement tools and techniques to verify that all parts conform to design specifications.
3. Manufacturing Process Control
a. Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs):
Develop detailed SOPs for every step of the manufacturing process, from machining and assembly to testing and packaging.
Ensure that all workers are trained in these procedures and understand the importance of adhering to them.
b. Precision Machining:
Use high-precision machining tools and CNC machines to manufacture critical components such as rotors, shafts, and housings.
Regularly calibrate equipment to maintain accuracy and consistency in production.
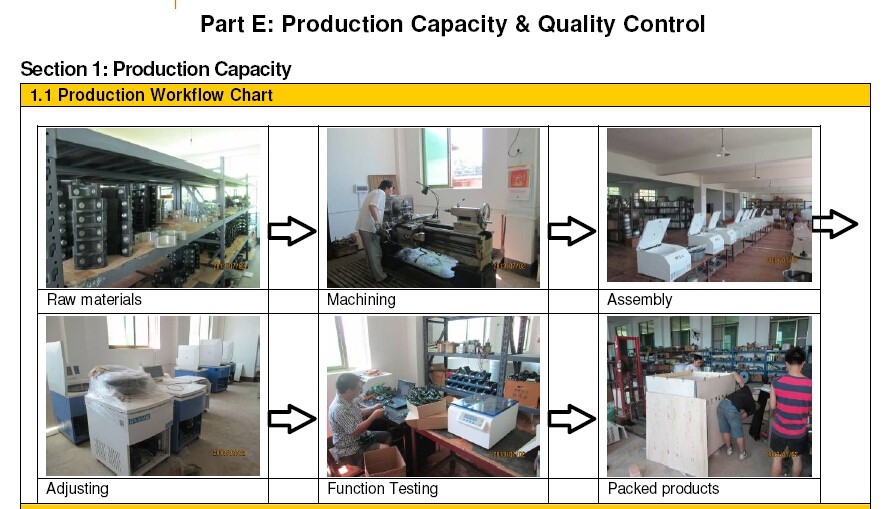
c. Assembly and Sub-assembly Control:
Implement a systematic assembly process that includes checkpoints for quality at each stage.
For sub-assemblies, such as the motor and control systems, ensure that they are tested independently before integration into the final product.
d. Environmental Controls:
Maintain a clean and controlled environment in the manufacturing area to prevent contamination, especially for centrifuges used in medical and laboratory applications.
Control temperature, humidity, and dust levels to ensure the stability of sensitive components.
4. Quality Assurance and Testing
a. In-process Quality Control (IPQC):
Perform quality checks during the manufacturing process to catch defects early. This includes dimensional checks, surface finish inspections, and alignment tests.
Implement Statistical Process Control (SPC) to monitor key parameters and identify trends that could indicate potential issues.
b. Final Product Testing:
Conduct comprehensive testing of each centrifuge before it leaves the factory. Key tests should include:
Balancing Test: Ensuring that the rotor is balanced to prevent vibration and ensure smooth operation.
Speed Verification: Testing the centrifuge at various speeds to verify that it meets the specified RPM range.
Temperature Control Test: For refrigerated centrifuges, test the cooling system to ensure it maintains the desired temperature range.
Safety Testing: Check safety features such as the lid lock mechanism, emergency stop function, and imbalance detection system.
Noise and Vibration Test: Ensure that the centrifuge operates within acceptable noise and vibration levels.
c. Documentation and Traceability:
Maintain detailed records of all testing procedures and results. This documentation should include serial numbers, test conditions, and the names of technicians who conducted the tests.
Implement a traceability system to track each centrifuge from raw material to final product, allowing for quick identification of issues if a problem arises after delivery.
5. Continuous Improvement and Feedback Loop
a. Customer Feedback:
Establish channels for receiving feedback from customers regarding the performance and reliability of your centrifuges.
Use this feedback to identify areas for improvement in design, manufacturing, and quality control processes.
b. Root Cause Analysis:
When defects or failures are reported, conduct a thorough root cause analysis to determine the underlying issues.
Implement corrective and preventive actions (CAPA) to address these issues and prevent recurrence.
c. Continuous Training:
Regularly train employees on new techniques, technologies, and best practices in quality control and manufacturing.
Encourage a culture of quality where every employee is responsible for maintaining high standards.
d. Technological Upgrades:
Stay updated with the latest advancements in manufacturing technologies and quality control tools.
Invest in new equipment or software that can enhance precision, efficiency, and reliability.
6. Regulatory Compliance and Certifications
a. Compliance with Standards:
Ensure that your centrifuges comply with relevant international standards such as ISO 9001 (Quality Management Systems), ISO 13485 (Medical Devices), and CE marking for European markets.
Adhere to specific industry regulations for centrifuges used in medical, pharmaceutical, or laboratory settings.
b. Certification and Audits:
Obtain certifications from recognized bodies to demonstrate your commitment to quality and safety.
Regularly undergo external audits to verify compliance with industry standards and regulations.
7. Packaging, Shipping, and Installation
a. Protective Packaging:
Design packaging that protects the centrifuge from damage during transportation. Use materials that cushion against shocks and vibrations.
Include moisture barriers and corrosion inhibitors if the centrifuge will be shipped or stored in humid environments.
b. Shipping and Handling:
Partner with reliable logistics companies that understand the delicate nature of centrifuges and can handle them with care.
Provide clear instructions for shipping and handling to prevent damage during transit.
c. Installation and Calibration:
Offer professional installation and calibration services to ensure that the centrifuge operates correctly at the customer’s site.
Provide detailed manuals and training for end-users to help them operate and maintain the centrifuge properly.
8. After-Sales Support and Warranty
a. Technical Support:
Provide robust after-sales support, including troubleshooting assistance, maintenance guidance, and spare parts availability.
Set up a helpline or online support system to address customer queries and issues promptly.
b. Warranty Services:
Offer comprehensive warranty coverage that reflects the quality and durability of your centrifuges.
Clearly define the terms of the warranty, including what is covered, the duration, and how customers can make a claim.
c. Continuous Monitoring:
Monitor the performance of centrifuges in the field through customer feedback and service reports.
Use this data to refine future designs and improve manufacturing processes.
Last and foremost, Customer feedback and feelings are also crucial, whether it is about quality or appearance, we need to convert these inputs into points that can be improved, this not only enhances customer satisfaction but also strengthens the manufacturer's reputation in a competitive market.