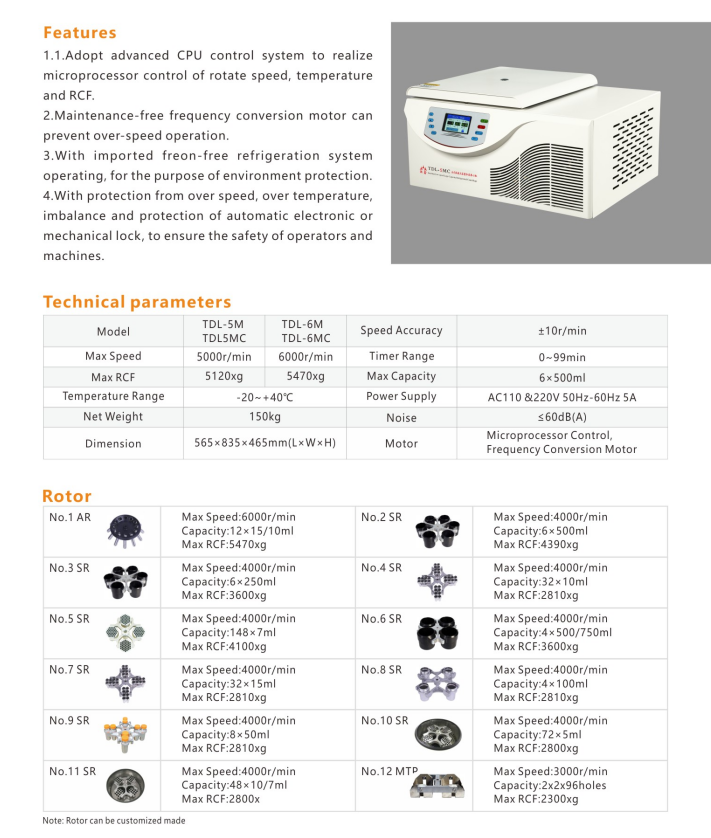
What is a Refrigerated Centrifuge and used for?
2024-07-20 09:44What is a Refrigerated Centrifuge and used for?
A refrigerated centrifuge is a specialized type of centrifuge designed to maintain low temperatures while spinning samples at high speeds. It combines the capabilities of a traditional centrifuge with a cooling system, typically using a compressor and refrigerant, to regulate and sustain temperatures as low as -20°C to -40°C. This feature is crucial for processing temperature-sensitive samples that could be degraded or altered by heat generated during high-speed centrifugation.
Applications of Refrigerated Centrifuges
Refrigerated centrifuges are used in various fields, particularly where the integrity of temperature-sensitive samples must be preserved. Some key applications include:
1. Molecular Biology
DNA, RNA, and Protein Purification:
Many molecular biology procedures involve the isolation and purification of nucleic acids and proteins, which are often sensitive to temperature changes. Refrigerated centrifuges prevent the degradation of these biomolecules during centrifugation, ensuring accurate and reliable results.
PCR and Cloning:
During polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and cloning processes, maintaining sample integrity is vital. A refrigerated centrifuge helps to keep enzymes and other reagents stable, improving the efficiency and accuracy of these techniques.
2. Biochemistry
Enzyme Assays:
Enzymes are particularly sensitive to temperature fluctuations. Refrigerated centrifuges are used to prepare enzyme samples, ensuring that they remain active and stable throughout the centrifugation process.
Metabolite Analysis:
For studies involving metabolites, which can be highly unstable, refrigerated centrifuges help maintain the chemical composition of samples, allowing for precise analysis.
3. Clinical Laboratories
Blood Component Separation:
In clinical diagnostics, refrigerated centrifuges are employed to separate blood components such as plasma, serum, and buffy coat layers while keeping them cool to prevent hemolysis and degradation of labile factors.
Cryopreservation Preparations:
For preparing samples for cryopreservation, such as cells, tissues, and other biological materials, refrigerated centrifuges ensure that the samples remain viable during the initial processing stages.
4. Pharmaceutical Industry
Drug Development and Stability Testing:
During the development and testing of pharmaceuticals, maintaining the stability of compounds is crucial. Refrigerated centrifuges are used to test the stability of drug formulations under various conditions, ensuring their efficacy and safety.
Vaccine Production:
Vaccine production often involves working with temperature-sensitive components. Refrigerated centrifuges help to keep these components stable during processing, ensuring the potency and effectiveness of the final product.
5. Environmental Science
Water and Soil Sample Analysis:
When analyzing environmental samples such as water and soil for pollutants, refrigerated centrifuges prevent the degradation of volatile compounds, ensuring accurate measurements.
Key Features of Refrigerated Centrifuges
Temperature Control:
The most distinguishing feature of a refrigerated centrifuge is its ability to maintain precise, low temperatures during operation. This is crucial for protecting sensitive biological and chemical samples.
High-Speed Capability:
Refrigerated centrifuges can operate at high speeds, generating significant centrifugal force while keeping samples cool. This combination of speed and temperature control is essential for many advanced laboratory techniques.
Versatile Rotors:
They often come with interchangeable rotors, allowing for a variety of tube sizes and types to be used, enhancing their versatility for different applications.
Digital Controls:
Advanced models feature digital interfaces that allow users to set and monitor temperature, speed, and duration with high precision. This ensures reproducibility and ease of use.
Safety Features:
Modern refrigerated centrifuges include safety mechanisms such as imbalance detection, automatic lid locks, and emergency shutoff to protect both the user and the samples.
Advantages of Refrigerated Centrifuges
Preservation of Sample Integrity:
By maintaining low temperatures, refrigerated centrifuges prevent the degradation of temperature-sensitive samples, ensuring that their biological and chemical properties remain intact.
Versatility:
Suitable for a wide range of applications across various scientific disciplines, refrigerated centrifuges are versatile tools in any laboratory.
Enhanced Accuracy and Reliability:
The ability to precisely control temperature and speed enhances the accuracy and reliability of experimental results.
Improved Efficiency:
With digital controls and programmable settings, refrigerated centrifuges streamline laboratory workflows, saving time and reducing the potential for user error.